The Earth’s inner core started slowing down over a decade ago, which has slightly affected the length of days. This phenomenon, commonly known as, Earth’s inner core rotation slowing, might possess significant implications for Earth’s magnetic and geological processes. This discovery sparked attention and controversy in the scientific community, contradicting previous understanding of Earth’s core mechanics. Let’s look at the specifics of this fascinating discovery as well as how it might affect our comprehension of Earth’s geography.
Latest Discoveries on Earth’s Inner Core Rotation
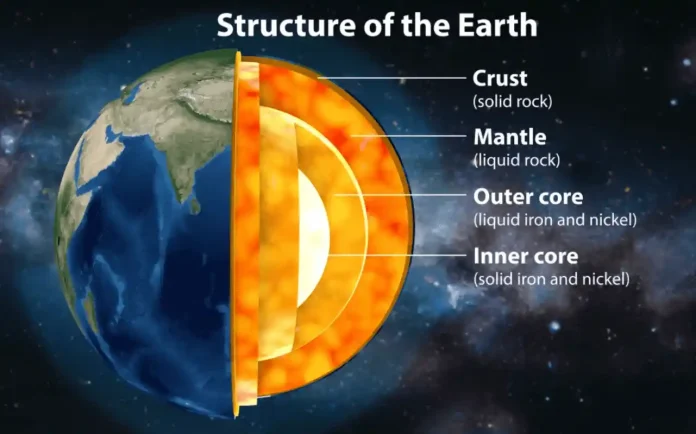
Recent study indicates a significant decrease in the inner core earth rotation, a solid metal sphere at its centre. Here arises a question: Has the Earth’s inner core slowed down? This unanticipated transition was identified by studying seismic waves from earthquakes, which revealed small but persistent shifts over the last decade. Research results reveal that the inner core’s rotation rate has dropped, raising significant concerns about the factors causing this shift and how it may affect Earth’s geophysical processes.
Scientists used cutting-edge seismological resources to detect the slowdown in the rotation of the inner core. They found changes in wave travel times after carefully examining seismic waves that penetrated and reflected off the inner core. When compared to prior seismic data, these small shifts revealed important information about the rotating mechanics of the inner core. Scientists used incredibly sensitive detectors and advanced data processing technologies to detect this slowing, revealing the complex processes happening deep inside the Earth.

Possible Causes of Earth’s Inner Core Rotation Slowing
There might be several possible causes for the shift in Earth inner core rotation:
Historical Transformations
Several researchers believe that the inner core’s rotation may follow a cyclical course that follows slowing and speeding up over long periods. Understanding historical trends and previous rotations may provide perspective for the current slowness.
Geodynamic Mechanisms
One main theory claims that changes in the dynamics of the Earth’s mantle and outer core might influence the rotation of the inner core. Complex interactions with the fluid outer core could impact the movement of the inner core.
Magnetic Field alterations
The rotation of the inner core is heavily influenced by the Earth’s magnetic field, which is formed by the movement of the molten iron in the outer part of the core.
Read More! Speed of Sound on Mars
Impacts of the Earth’s Inner Core Rotation Slowing
Has the core of the Earth slowed down? Yes! Has it impacted the atmosphere on earth’s surface? Yes! Let’s find out how:
- Earth’s Magnetic Field
Drop in the inner core’s rotation might affect the intensity of the Earth’s magnetic field, leading to geomagnetic changes and affecting navigational mechanisms.
- Geological and Climate Processes
Rotation decrease might be having a consequence on geological processes by changing convection in the mantle, which might impact tectonic movements and transference of heat. These alterations might have a secondary impact on climate patterns, which could give rise to greater eruptions of volcanic gases and atmospheric disturbances.
Explore More! Earth’s Magnetic Field Explained
- Seismic Activity Disturbance
A slowing of the Earth’s inner core rotation might change stress distribution, mantle convection, and pressure conditions, thereby affecting seismic activity. This might result in more earthquakes, alterations in tectonic plate movements, and long-term changes in seismic patterns.
The dramatic Earth’s inner core rotation slowing can lead to significant implications for how the Earth operates. This process holds significant impacts not only on Earth’s magnetic field, but also on seismic activities and geological processes. Addressing these consequences is essential for preparing for future geological and ecological shifts, as well as improving readiness and resistance to seismic risks.